Have no membrane-bounded organelles. A cub tiger begins to grow.
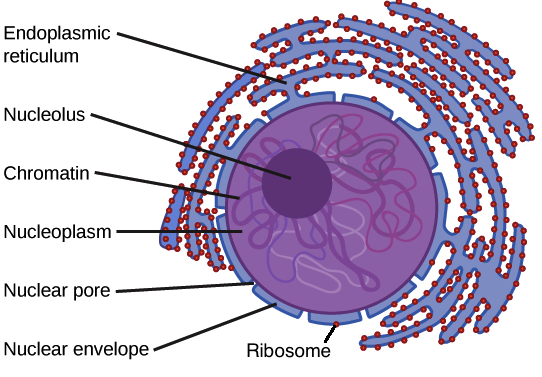
Nucleus And Ribosomes Article Khan Academy
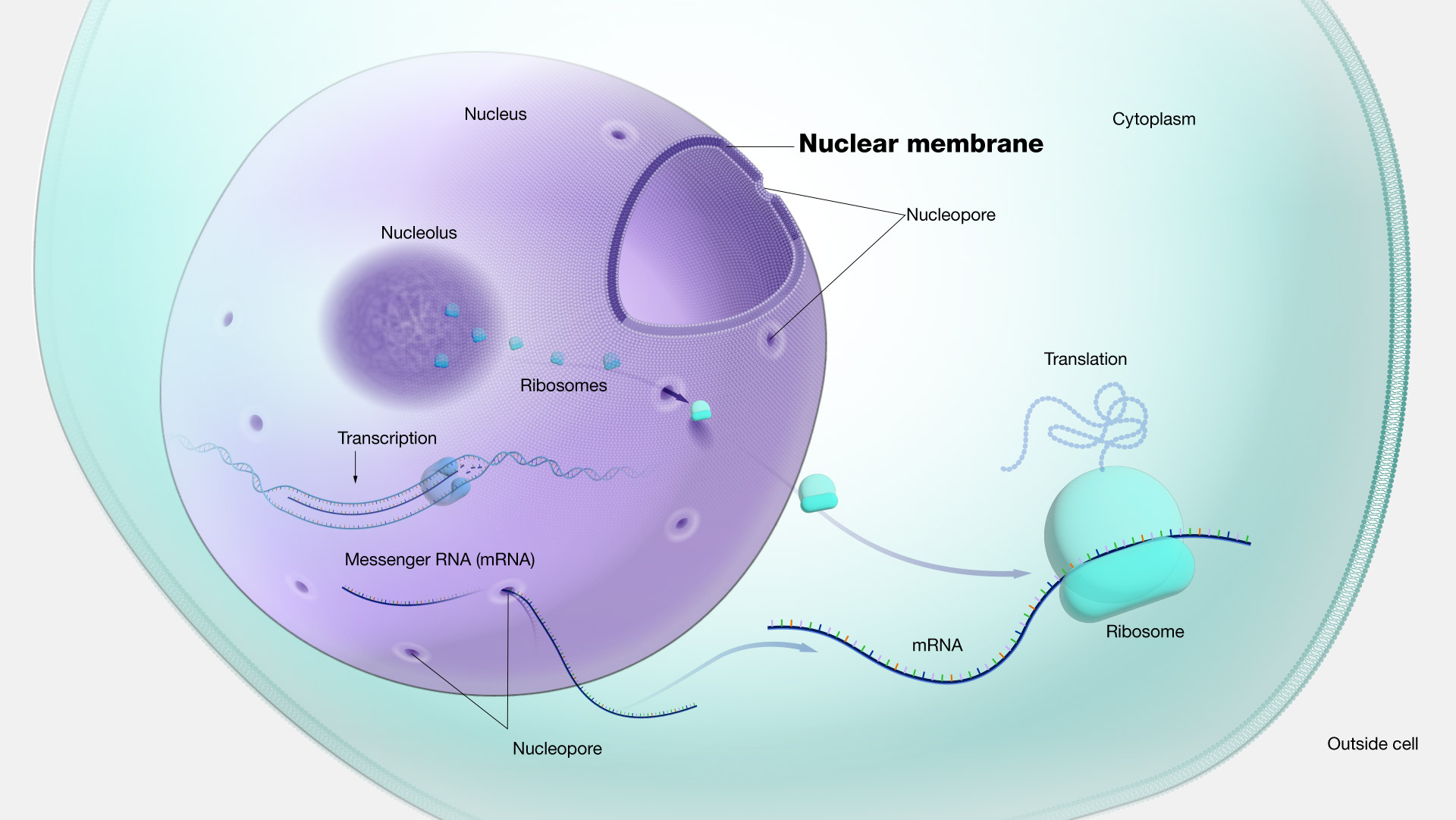
The endomembrane system is composed of the different membranes that are suspended in the cytoplasm within a eukaryotic cell.
. A dish of animal cells was grown in the presence of radioactive phosphorous. In which cellular structure s would you predict the. The nuclear membrane does not perform endocytosis and exocytosis but does have transport pores The nuclear envelope is a double layer consisting of two lipid bilayers that are folded together while the plasma membrane consists of a single lipid bilayer.
It is rigid and impermeable. B The nuclear membrane carries chromosomes from their original position to the center of the cell as metaphase occurs. Most cells have a short life span.
The nuclear membrane is also known as the nuclear envelope. In which stage of the cell cycle is this process reversed. Long-lasting proteins are likely to make the cell cancerous.
It contains pores that allow only certain molecules to. The membrane also allows for water to be pumped. It is identical in composition to the cell membrane.
The students placed an X for each structure that was viewed for each cell on the table shown. It allows all molecules to pass across it into the nucleus. _____ bind s to DNA enhancer regions.
Simple diffusion A targeting sequence that interacts with a carrier protein Vesicular transport followed by delivery via fusion with the nuclear membrane An N-terminal targeting sequence that is cleaved during transport Co-translational transport using ribosomes attached. The phosphorous largely ended up in nucleotides inside the actively growing animal cells. Students use a microscope to look for structures present in four different cells.
Both control what goes in and out of the nucleus or of the cell. Which cell that was viewed is most likely a prokaryote. Here we show that PREP1 binds to promoter regions of inner nuclear membrane proteins SUN1 SUN2 and LAP2 genes and upon reduction of PREP1 the expression of these genes and proteins is affected.
This allows cells to maintain a higher concentration of sodium ions out the outside of the cell. It is defined as the double lipid bilayer membrane which surrounds the genetic material and nucleolus of the eukaryotic cell. Simple diffusion A targeting sequence that interacts with a carrier protein Vesicular transport followed by delivery via fusion with the nuclear membrane An N-terminal targeting sequence that is cleaved during transport Co-translational transport using ribosomes attached.
The perinuclear space separates the outer and inner membrane. Most proteins are used only once. The cell membrane is a lipid bilayer that prevents that passage of water and ions.
_____ bind s to DNA enhancer regions. A nuclear membrane is composed up of two membranes an inner and an outer membrane. The complete nuclear membrane includes four series of phospholipids.
C As chromosomes disappear the nuclear membrane recreates new chromosomes that line up along the center of the cell. This means that all of its contents are surrounded by membrane made of phospholipids. Early in mitosis the nucleus nucleolus and nuclear envelope begin to dissolve in preparation for cell division.
Which of these best describes the nuclear membrane. The outer membrane works by the rough endoplasmic. In which of these stages is mitosis most important.
Both membranes consist of phospholipids that are organized in a bilayer. Which of the following BEST describes the transport of nuclear proteins across the nuclear membrane. The space between these two membranes is known as perinuclear space.
Bacterial cells are prokaryotic. Choose the correct answer. Cells lack the raw materials to make most of the proteins they need.
The nuclear membrane or nuclear envelope is a specialized membrane consisting of two lipid bilayers which surrounds the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell. Unlike a typical eukaryotic cell _______ they. The endomembrane system carries out critical functions in the cell.
Which of the following BEST describes the transport of nuclear proteins across the nuclear membrane. Once the nuclear membrane completely disappears chromosomes are able to line up along the center of the cell. These phospholipids align tail-to-tail in two distinct sheets.
34 Questions Show answers. The two lipid bilayers are known as inner nuclear membrane and outer nuclear membrane. Like all organelles in a eukaryote the nucleus is membrane-bound.

0 Comments